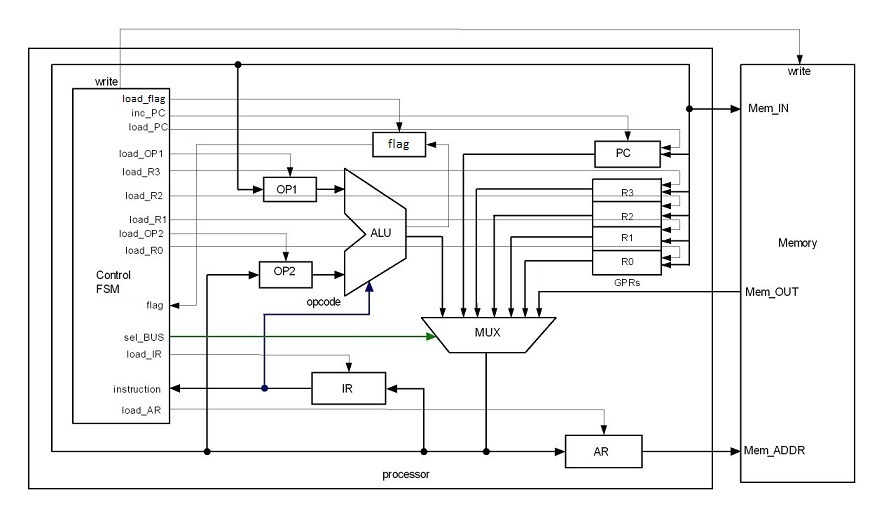
Architecture
- The CPU has a single 8-bit bus which is shared for both data and instructions.
- The CPU is based on Von-Neumann architecture, so both data and address are stored in same memory.
- There are four 8-bit general purpose registers: R0, R1, R2 and R3.
- It has an instruction register (IR) to hold the instruction for the next operation. The Control signals are generated by a state machine according to the specific combination of bits in the instruction register. These control signals are applied to various registers, program counter and memory.
- It has a program counter (PC) which auto increments after each operation to point to the next instruction or data present in the memory.
- It has an address register (AR) to store immediate address of the memory location to be accessed during a particular operation.
- As of now the ALU performs limited operations like ADD, SUB, AND and NOT. The two operand registers OP1 and OP2 are used to give inputs to the ALU.
- There is also a flag register to store information about zero and negative condition required for branch operations.
- The Multiplexer allows the output from registers, pc, alu and memory based on the select bits from the FSM.
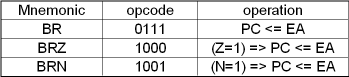
- Two branch operations are possible: unconditional branch and branch if zero.
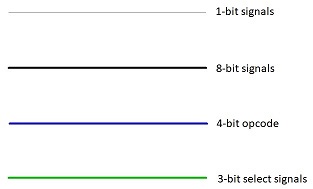 Note that I have used different colored wires to represent signals. 1-bit signals are control signals in and out of the FSM which are applied to various registers and PC.
8-bit signals are data, instruction, address travelling on the bus. 4-bit opcode goes into the ALU to specify the operation. 3-bit signals are mux select inputs from the FSM.
Note that I have used different colored wires to represent signals. 1-bit signals are control signals in and out of the FSM which are applied to various registers and PC.
8-bit signals are data, instruction, address travelling on the bus. 4-bit opcode goes into the ALU to specify the operation. 3-bit signals are mux select inputs from the FSM.
Instruction set
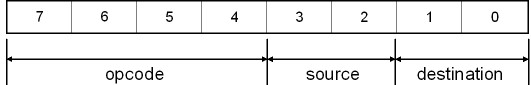
The instruction set is very simple. The first nibble is the opcode and the low order nibble specifies two registers for source and destination. The instructions are of two type:
- A format instruction
- B format instruction
The instruction set above is for A-format instruction. I have taken source as ra and destination as rb. These ra and rb can be any of the four general purpose registers.
A-format instructions:
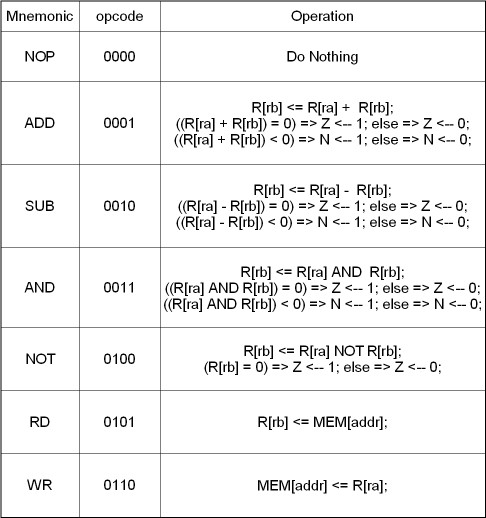
B-format instructions are two bytes and are used for branch instructions. The first byte specifies the operation and the next byte is the address to be loaded into the PC for branch operations.

B-format instructions:
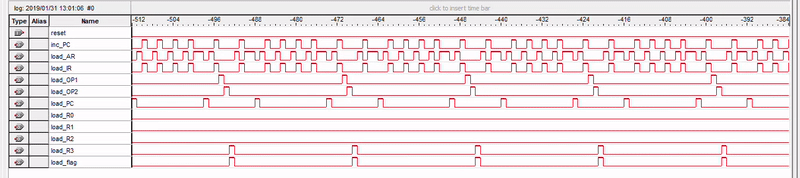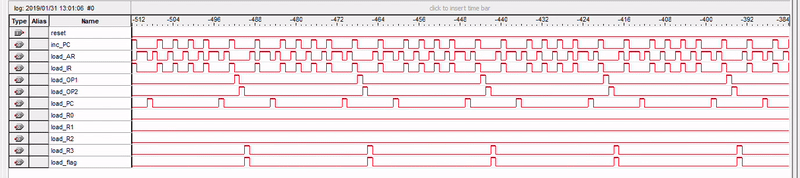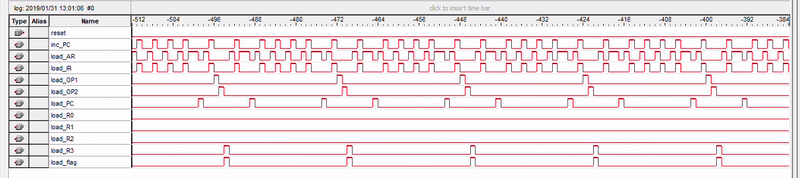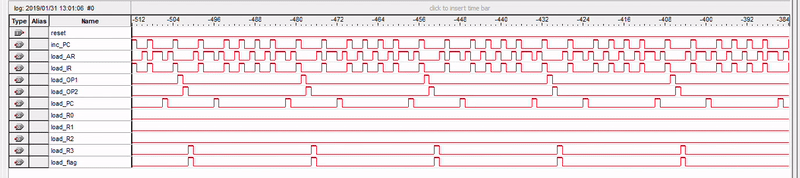
Simulation
Subtracting 3 from 5
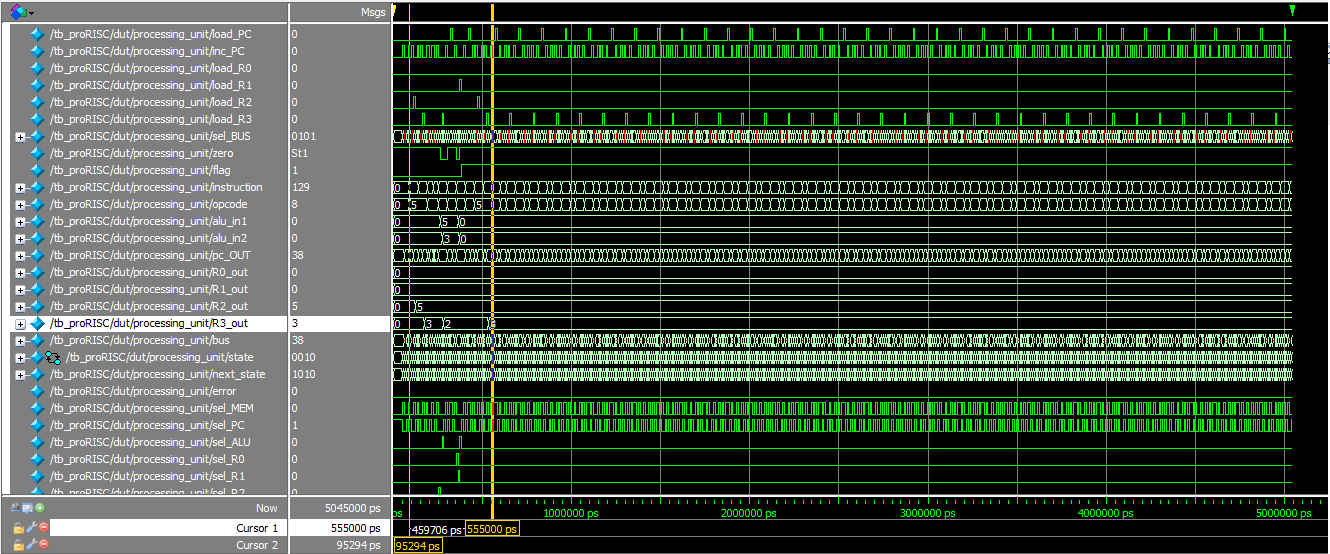
Observing various control signals using SignalTap Logic Analyzer